Simply put, the biological clock, also known as the circadian rhythm, is an internal body’s rhythm. It signals from deep within the brain, creating a 24-hour cycle that helps determine when to wake up and when to go to sleep.
1. How Does the Biological Clock Work?
The biological clock is a 24-hour internal cycle that not only controls our sleep but also regulates several internal systems such as hormones, eating habits, body temperature, sensitivity, mood, and digestion, aligning them with the rotation of the Earth.
Light is the main factor affecting the biological clock
Research shows that our biological clock, that is,the circadian rhythm, is closely related to light.
The circadian rhythm activates many mechanisms in the brain and body during the day to keep you alert and awake; however, these processes gradually slow down at night, eliminating the alertness so that the body can prepare to go to sleep.
Therefore, light is the most important body clock regulator.
What Happened After Cutting off Daylight
Although sunlight is a major factor affecting the circadian rhythm, it is not the only one. Other factors also help regulate the circadian rhythm or are used to adjust it in the absence of sunlight.
In 1938, Professor Nathaniel Kleitman and his research assistant Bruce Richardson from the University of Chicago conducted a six-week experiment in a pitch-dark cave.
They discovered that after cutting off the daylight, their biological rhythms of wakefulness and sleep did not become disordered but instead showed a predictable, repetitive cycle. The cycle was not exactly 24 hours, but slightly longer than 24 hours.
2. What Controls Your Sleep?
Sleep is a physical instinct, but certain conditions are needed to fall asleep.
This involves two main factors controlling whether we are awake or asleep: One is the signal sent by the biological clock deep in our brain, that is, the circadian rhythm, which makes you feel tired or awake during the typical nighttime and daytime hours.
The other factor is a chemical that accumulates in our brain —— Adenosine
- Adenosine and Sleep Pressure
Adenosine creates “sleep pressure.” From the moment you wake up, your body begins to accumulate adenosine. The longer you are awake, the more sleep pressure builds up, making you want to sleep. Once you are detected to be in a sleep state, adenosine levels start to decrease until they disappear, and your sleep pressure will be released.
- The Relationship Between Circadian Rhythm and Sleep Pressure
The balance between circadian rhythm and sleep pressure determines how alert and focused you are during the day and how tired and when to go to sleep at night.
Unlike “sleep pressure”, circadian rhythm never cares whether we are awake or asleep. It slowly and rhythmically rises and falls strictly according to the day-night changes.
Regardless of how much sleep pressure your adenosine causes, the 24-hour circadian rhythm will still circle as usual, ignoring whether you are extremely sleep-deprived.
This explains why we can’t simply fall asleep at any time during the day after being awake for 24 hours, as we are trying to fight against the circadian rhythm in our body, even when sleep pressure is very high. Body’s internal clock urges us to work at sunrise and rest at sunset.
3. How Does Melatonin Affect Your Sleep?
There’s a major misconception about melatonin that it aids in sleep. In reality, melatonin has almost no effect on the formation of sleep itself. The doses of melatonin found in over-the-counter products are quite small, and many act merely as sleep placebos.
Whenever night falls, the pineal gland located deep in the back of the brain begins to release melatonin. The function of melatonin acts like a powerful loudspeaker, announcing a message to the brain and body: “It’s dark now.”
Once sleep starts, the concentration of melatonin gradually decreases throughout the night. By dawn, when sunlight penetrates the eyelids and reaches the brain, the pineal gland shuts off the release of melatonin, signaling to the brain and body that “sleep is over.”
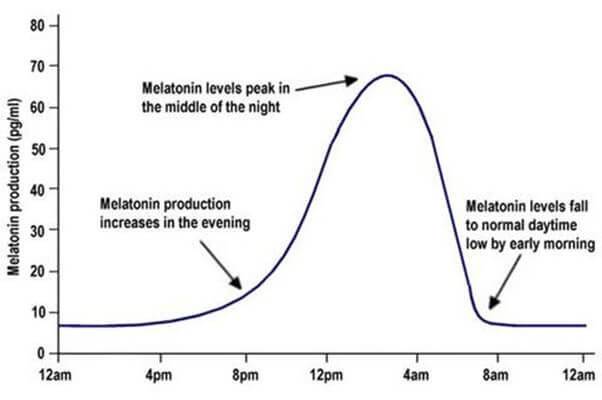
You might have realized by now that melatonin is an essential part of the 24-hour circadian rhythm. Light is a regulator of the biological clock, and similarly, light influences the production and fading of melatonin.
The blue light in the daylight can suppress the secretion of melatonin, boosting serotonin production, this enhancing alertness and sensitivity; however, after dark, blue light becomes harmful.
If you use electronic devices after dusk, the blue light emitted can suppress the secretion of melatonin in your body, and the brain and body may not receive enough “it’s dark” signals, naturally delaying your biological clock. This is why blue light is often referred to as one of the modern sleep killers.
4.What Type of Sleeper Are You?
Although humans exhibit a fixed 24-hour circadian rhythm, everyone’s peaks and troughs differ significantly.
Some people reach their peak of alertness very early in the day, and their sleep troughs come early after nightfall. These individuals are known as “early bird” and make up about 40% of the population, typically preferring to go to bed and wake up early.
Others are “night owls,” making up about 30% of the population, they usually go to bed late and waking up late the next morning or even the next afternoon. The remaining 30% fall somewhere between these two types.
Sleep type is genetically determined, and modern work hours are particularly unfavorable for night owls. No matter how they try, night owls typically can’t fall asleep early at night. When still in their deep sleep early in the morning, they have to get up to go work while their brain are still fuzzy.
5.Conclusion
After four billion years of evolution, the biological clock cycle has become an instinct in living beings. Any attempt to override one’s own body clock can lead to severe health issues. Understanding your circadian rhythm is crucial for leading a healthy life.
